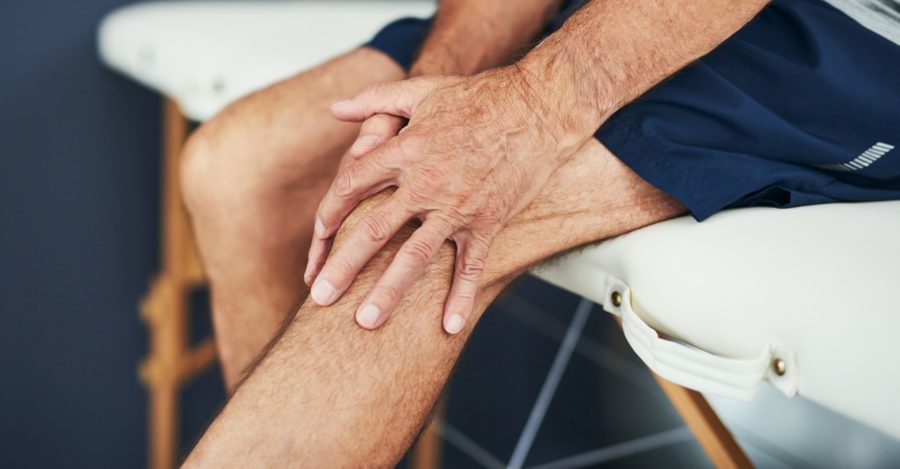
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder which affects the immune system and attacks body tissue. With 1 in 4 American adults suffering from diagnosed arthritis there has never been more importance in early detection and treatment.1 The early signs are easy to spot once you know them so learn the symptoms now.
What Exactly Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
We’ve all heard the arthritis term in our lifetimes but there are different types of this condition that have arisen over the years with more detection available. Rheumatoid Arthritis is the most common and is essentially an autoimmune disease that attacks synovial tissues within the joints. Autoimmune conditions occur when the bodies own immune system is confused with its own tissues.2 This confusion leads to a creation of antibodies which begin to affect the tissues within our joints mistaking them for foreign invasive cells.
Who Is At Risk Of Developing This Condition?
Rheumatoid Arthritis is one of the most common autoimmune diseases in the country right now and patients are widespread. Rheumatoid Arthritis tends to affect people more with age and the most common age bracket for this condition is 60 years of age and older. Gender is another factor which has been noted with woman being up to 2-3 times more likely to develop Rheumatoid Arthritis in their lifetime.3 Other factors of those being at risk of developing this condition include genetics, smoking and obesity. It is strongly recommended that if you’re feeling any of the signs and symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis that you give up smoking and follow a healthy diet.
Family History Of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Recent studies have found that there is a gene called HLA or (human leukocyte antigen) class II genotypes which can make your arthritis worse. These gene types combined with smoking and obesity can rapidly onset the occurrence of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
The Early Warning Signs You Must Pay Attention Too
There are a range of symptoms noted by medical professionals that arise in early cases of Rheumatoid Arthritis. It is encouraged that if you experience any of the following symptoms to contact your doctor immediately to discuss options.
- Swelling – Your joints begin to swell or have a red appearance on a regular basis, specifically not exercise induced.
- Pain and Stiffness – Noticing general stiffness and pain in joints especially when waking up.
- Multiple Locations – Experiencing pain and stiffness in more than one location such as fingers and knees.
- Symmetrical – If you experience swelling, pain and stiffness in both the left and right sides of the body.
- Reduced Range of Motion – In early stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis the joints are mildly restricted. Noticing you can’t move your arms in circles or knees are limited in motion tend to be early warning signs.
Which Joints Are The Most Affected By This Condition?
- Wrists – The wrist joint can be affected in the disease early and repetitive motion can cause the wrist joint to become inflamed and painful.
- Knees – Rheumatoid Arthritis can affect the knees early in its appearance which is noticeable in both knees of patients.
- Ankles – Inflammation of this condition can run down the knee into the ankles causing swelling and stiffness making it difficult to walk.
- Fingers – One of the most commonly affected and noticed by patients is the finger joints. Holding objects and gripping can become difficult making it an easier one to notice for patients.
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed?
If a patient is showing early signs and symptoms of this autoimmune condition a doctor may forward the patient to a rheumatologist. A rheumatologist is a specialist who works with arthritis and other diseases of the joints, bones and muscles. Often a blood test will be ordered and it will look for specific antigens in the blood which may indicate Rheumatoid Arthritis. These factors include Rheumatoid factor, anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (CCP), Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-Reactive Protein (CRP).
Treatments For Rheumatoid Arthritis?
If a patient is diagnosed with this condition there are multiple treatments available to manage this condition however it is important to note there is no exact cure just yet. There are however many medications or natural remedies which can dramatically reduce pain and swelling making it more manageable. Such medications include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – These are some of the most common medications for arthritis and work by reducing inflammation.
- Corticosteroids – Another medication used in reducing inflammation of the joints.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) – DMARDs are used in slowing down the progress of Rheumatoid Arthritis and are a standard procedure in patients wanting a pharmaceutical option.
Follow Diet And Lifestyle Changes
Another important aspect for managing the affects of Rheumatoid Arthritis is making appropriate lifestyle and diet changes. As suggested before obesity and smoking are major implications for arthritis and should be considered in a treatment program. Eating a diet rich in omega 3 foods like salmon, cod liver oil and walnuts may help to reduce inflammation. Eating anti oxidant rich foods like berries, coffee, dark chocolate, green tea may help to ease the bodies response of swelling.
Learn The Early Signs And Contact A Local Specialist Now
If you’re experiencing any of the early warning signs then seeing a specialist is your best defence against further developing Rheumatoid Arthritis.. Keep your family safe and well informed with routine check ups can safeguard your life and keep you in a healthy state of being. Professionals are available across the nation and ready to discuss options for this condition.
See Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Reference: